Pulse oximeters are essential tools in the healthcare field, allowing for precise measurement of oxygen saturation levels in the bloodstream. With the ability to provide instant results, these devices are crucial for monitoring oxygen levels in different medical environments. Whether you need one for personal use, seek medical pulse oximeters for professional use, or for specific conditions such as sleep apnea or COPD, here’s what to consider when shopping.
How Does a Regular Pulse Oximeter Work?
Hemoglobin, a pigment found in red blood cells, combines with oxygen during the process of oxygenating blood in the lungs, resulting in oxyhemoglobin.
Oxyhemoglobin can absorb a significant amount of infrared light as it passes through. The concept behind pulse oximetry measurement is based on the absorption of infrared radiation by oxyhemoglobin.
In practical terms, a light-emitting diode emits infrared light to a photodiode through a capillary. The amount of infrared light absorbed by the capillary is directly proportional to the concentration of oxyhemoglobin.
Types of Oximetres
Finger Pulse Oximeter
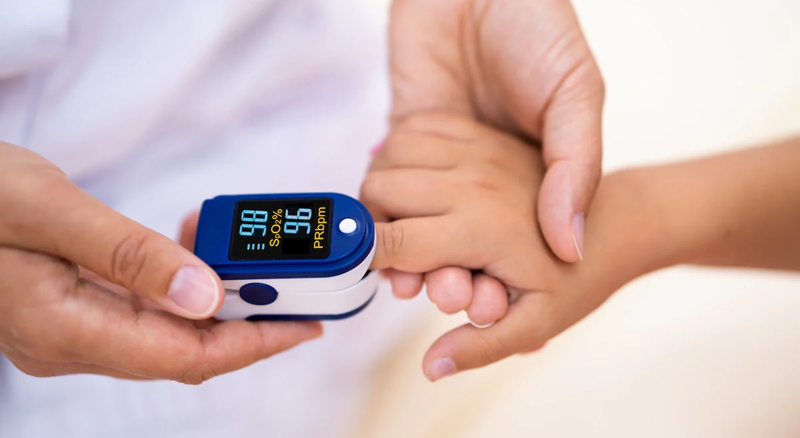
Finger medical pulse oximeters are small and portable devices that can be attached to the fingertip. They’re commonly used to quickly check oxygen saturation levels and heart rate. Finger pulse oximeters are ideal for home use and for individuals who only need occasional monitoring.
Portable
Portable oximeters provide increased mobility and are made for users who need to monitor their oxygen levels while on the move. They’re suitable for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals who need continuous monitoring during physical activities.
Digital
These use advanced technology to give precise and accurate readings. They often have a digital display that shows oxygen saturation levels and heart rate. Digital oximeters are easy to use and can be used in various settings, including at home and in healthcare facilities.
Handheld Pulse Oximeter
Handheld pulse oximeters are larger than finger oximeters and offer more features for advanced monitoring. They provide continuous monitoring of oxygen levels and heart rate, making them valuable tools in hospitals and emergency medical services.
Pediatric
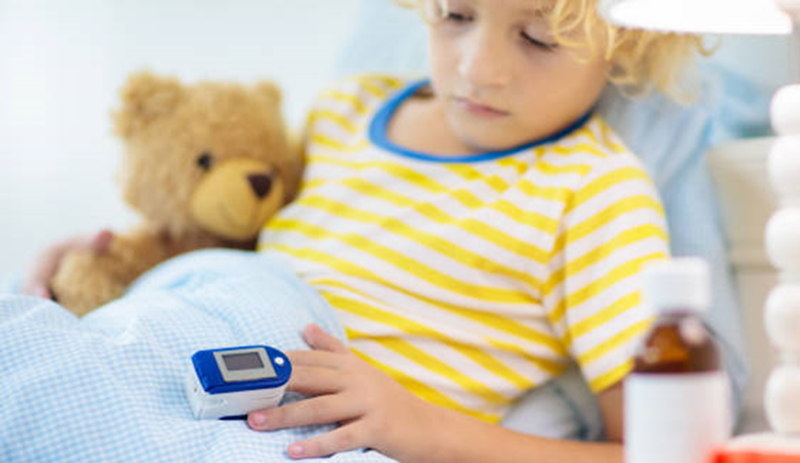

Pediatric pulse oximeters are specially designed for children. They come with smaller sensors to ensure a comfortable fit for young patients. Pediatric pulse oximeters provide accurate readings and are commonly used in pediatric healthcare settings.
How to Choose It?
Primary Criteria
- Application – oximeters can be used in various settings, including hospitals, homes, neonatal/pediatric units, sports, and veterinary fields. It’s essential to choose a device that suits the intended application.
- Type of oximeter – there are two main types of pulse oximeters. Fingertip pulse oximeters have the monitor integrated into the clip-on sensor, making them portable and convenient for both individual and hospital use. Pulse oximeters with a separate sensor have the monitor connected to the sensor via a cable. While these devices may be less practical for individual use, they provide more reliable measurements and are suitable for hospital wards.
- Measurement reliability – it’s recommended to select a pulse oximeter that has obtained CE certification and meets the ISO 8061-2-61 standard. The user should also refer to the manufacturer’s instruction manual to determine the exact margin of error. The number of sensors present on the device also affects measurement reliability.
- Autonomy – if you’re going to use a pulse oximeter multiple times a day, its autonomy becomes essential. Most devices are battery-operated, and the level of autonomy depends on features such as powerful backlighting of the display screen (which consumes more energy) and the presence of an automatic shutdown function (which saves battery usage).
Secondary Criteria
- Readability is enhanced by features like a strong backlight, a display that can be viewed from multiple angles, anti-reflective glass, and a large, high-contrast number display.
- Complementary measures refer to the ability of the pulse oximeter to work in conjunction with a capnograph or a heart rate monitor, as well as its capability to measure heart rate.
- Device reliability is crucial, especially for professionals like firefighters or mountaineers, and includes resistance to shocks, dust, and water.
What to Consider for Different Applications - Athletes – these people often need pulse oximeters to monitor their oxygen levels and heart rate during intense physical activities. Seek out durable and reliable devices with accurate readings to assist in training and performance tracking.
- For sleep apnea – it can provide valuable information on oxygen levels during sleep. Opt for a device with comfortable sensors and dependable data recording capabilities.
- For COPD patients – Monitoring oxygen levels is critical for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Using an oximeter specifically designed for COPD patients enables them to closely monitor their oxygen saturation levels and identify any potential exacerbations.
- For respiratory monitoring – consider devices with continuous monitoring capabilities and options for data storage for precise and long-term tracking.
- For fitness tracking – choose wearable pulse oximeters; look for devices that offer activity-tracking features, smartphone connectivity, and extended battery life for convenient monitoring during workouts.
How to Use It?
Using a pulse oximeter is a straightforward process that remains consistent across different devices. The key steps to follow include:
- Ensure that the sensor and LED transmitter are clean by using an alcohol or soap solution.
- Place the sensor on a finger, typically the index finger, ensuring there is no nail polish or grease present.
- Normal blood oxygen saturation levels range between 95% and 100%. Levels below 95% should be monitored closely, while levels below 90% are considered critical.
- After taking a measurement, store the device in its case in a dry, room temperature location away from direct light to maintain battery life and ensure accurate readings.
